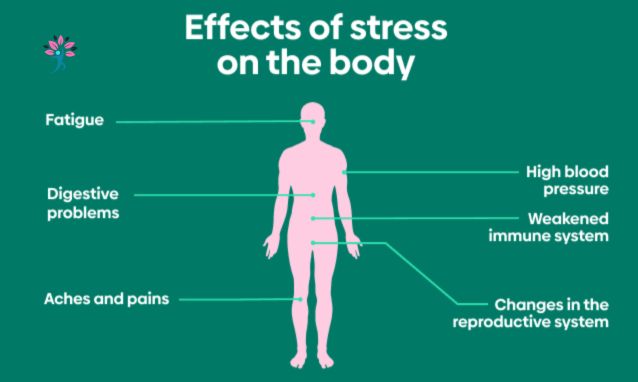
Stress and pain are deeply interconnected. When you experience stress, your body responds by increasing muscle tension, altering your nervous system, and heightening your sensitivity to pain. This can lead to chronic pain conditions, migraines, and overall discomfort. Understanding the connection between stress and pain can help you take control of your well-being and adopt effective physical self-care strategies.
The Science Behind Stress and Pain
How Stress Triggers Pain in the Body
Stress activates the body’s fight-or-flight response, releasing cortisol and adrenaline. While these hormones help in emergencies, chronic stress keeps them elevated, leading to:
- Muscle Tension: Tight muscles can result in headaches, neck pain, and back pain.
- Inflammation: Prolonged stress increases inflammation, worsening conditions like arthritis and fibromyalgia.
- Nerve Sensitivity: Stress can make the nervous system hypersensitive, increasing pain perception.
- Weakened Immune System: Stress negatively affects immunity, making the body more susceptible to chronic pain conditions.
The Link Between Chronic Stress and Chronic Pain
Chronic stress disrupts the balance of neurotransmitters, reducing your body’s ability to manage pain. Studies show that conditions like tension headaches, fibromyalgia, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) worsen under stress. Additionally, stress can impact hormonal balance, further aggravating chronic pain conditions.
Common Pain Conditions Worsened by Stress

1. Back Pain and Stress
Stress-induced muscle tension commonly causes back pain. Poor posture due to stress-related tension can worsen spinal alignment and lead to chronic discomfort. Regular stretching, massage, and physical therapy can help relieve tension and prevent long-term complications.
2. Migraines and Tension Headaches
Emotional and physical stress is a well-known trigger for migraines. Increased muscle tightness in the shoulders and neck contributes to tension headaches. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, hydration, and a proper sleep schedule can significantly reduce occurrences.
3. Joint Pain and Arthritis
Inflammatory responses from stress intensify arthritis symptoms and joint pain, making movement more difficult. Engaging in low-impact exercises like swimming or yoga can help alleviate pain and improve joint flexibility.
4. Stomach Pain and Digestive Issues
Stress affects gut health, leading to conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and acid reflux, which cause stomach cramps and bloating. Eating a balanced diet rich in fiber and probiotics can help improve gut health and reduce pain.
5. Fibromyalgia and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
People with fibromyalgia experience amplified pain when under stress. Managing stress through cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), meditation, and physical therapy can significantly help.
Effective Ways to Relieve Stress-Induced Pain

1. Practice Deep Breathing and Meditation
Deep breathing exercises, like diaphragmatic breathing and mindfulness meditation, activate the parasympathetic nervous system, reducing stress and lowering pain perception. Even a few minutes of deep breathing each day can have a significant impact on overall well-being.
2. Engage in Physical Activity
Regular exercise releases endorphins, which are natural painkillers. Activities like yoga, stretching, and walking relieve tension and reduce chronic pain. Even light movement, such as tai chi, can help maintain flexibility and reduce stiffness.
3. Prioritize Quality Sleep
Lack of sleep amplifies stress and pain. Create a bedtime routine, reduce screen time before sleep, and use relaxation techniques to improve sleep quality. Learn more about the best sleeping positions for chronic pain to enhance rest and recovery. Proper sleep hygiene, including avoiding caffeine before bed and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, can help improve sleep duration and quality.
4. Adopt a Healthy Diet
Anti-inflammatory foods like leafy greens, omega-3-rich fish, and nuts help reduce pain and support stress management. Avoid processed foods, excess sugar, and caffeine, as they can worsen stress-related inflammation and pain symptoms.
5. Use Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat relaxes tense muscles, while cold therapy reduces inflammation and numbs sharp pain. Alternating between heat and cold can be particularly effective for chronic pain relief.
6. Consider Professional Therapies
Massage therapy, acupuncture, and chiropractic care are effective for managing stress-related pain. Discover how acupuncture for pain relief can help reduce tension and chronic discomfort naturally. Many people also benefit from physiotherapy, osteopathy, and myofascial release therapy.
7. Manage Emotional Stress
Practice journaling, talk therapy, or engage in hobbies that bring joy and relaxation. Building emotional resilience can help you manage stress and reduce pain levels. Seeking professional counseling or therapy can provide guidance on stress management techniques.
8. Hydration and Supplements
Staying hydrated is crucial for muscle function and reducing cramps. Supplements like magnesium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids can help manage inflammation and improve pain management.
9. Improve Workplace Ergonomics
Long hours of sitting and poor posture can worsen stress-induced pain. Adjusting chair height, using ergonomic keyboards, and taking frequent breaks can prevent strain-related pain.
Final Thoughts
Stress and pain are closely linked, but you can take control of your well-being with the right physical self-care strategies. By understanding how stress affects pain and implementing these pain relief techniques, you can improve your quality of life and achieve long-term health. The key is to be consistent with stress-reduction techniques, listen to your body’s signals, and make adjustments as needed.
For more expert advice on physical self-care and pain relief, visit Venzec.